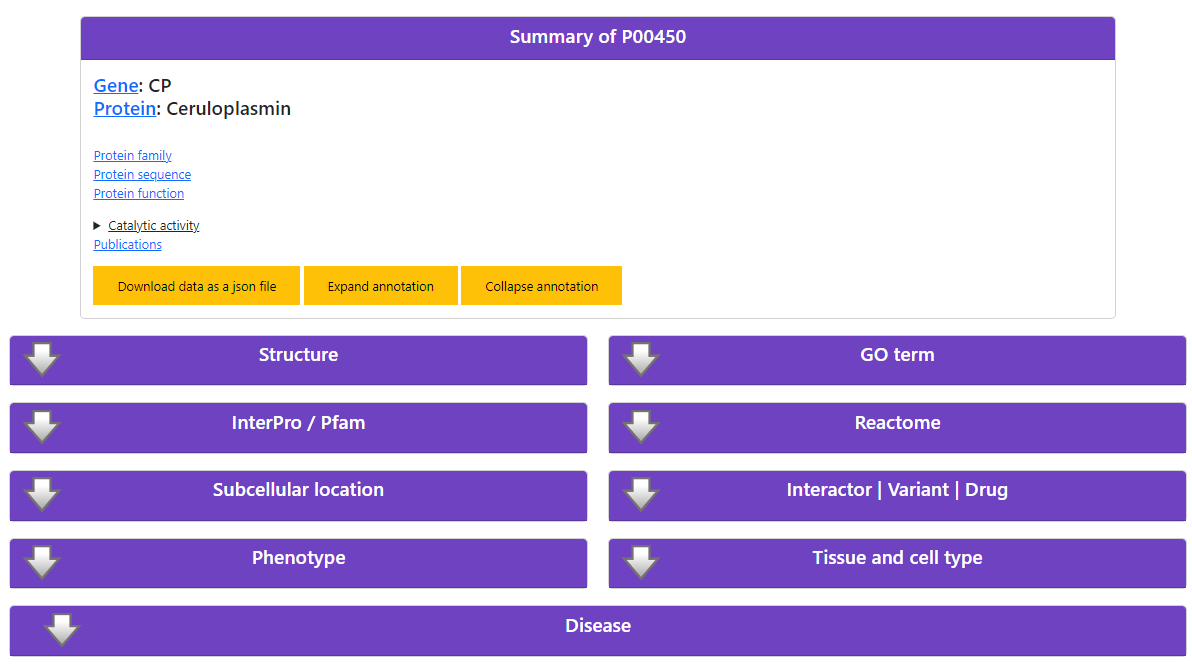
We start our analysis searching the protein in DAR, using the UniProt accession number "P00450".
The protein in an enzyme associated with 1 EC number, 1 disease, 4 Reactomes and 3 reactions (Figure 1).
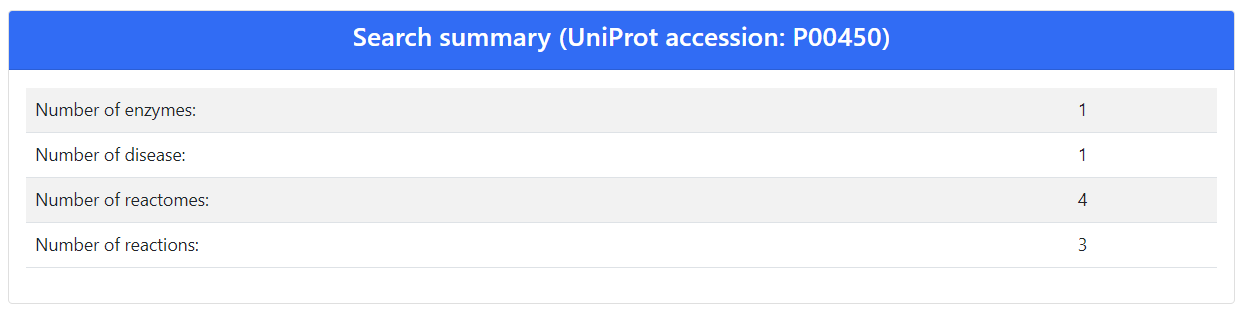
Details of Ceruloplasmin annotation in terms of identifiers for pathways, reactions and diseases are reported in the "Search results" table (Figure 2).
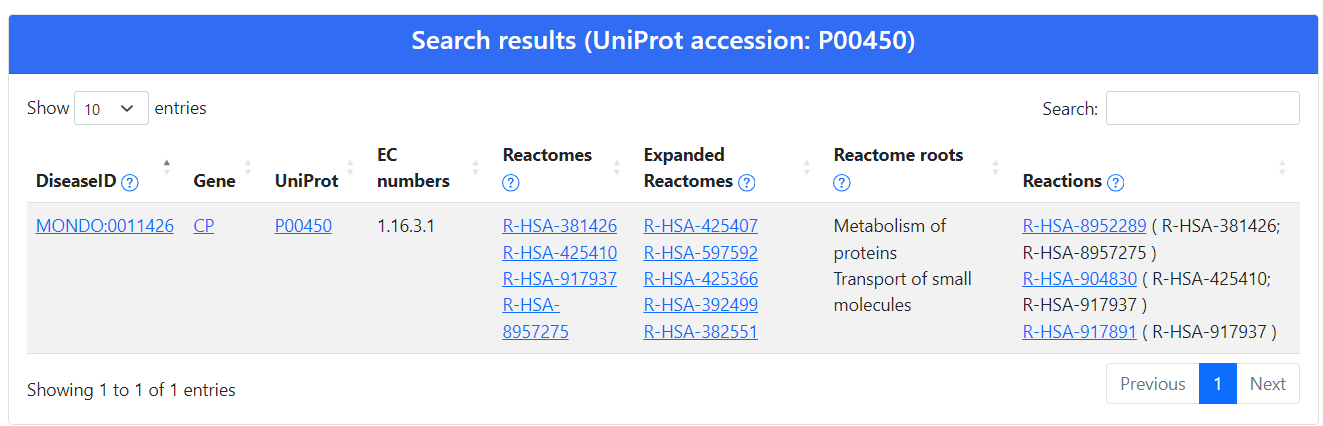
To retrieve more information about the disease association, we search eDGAR using the same UniProt accession
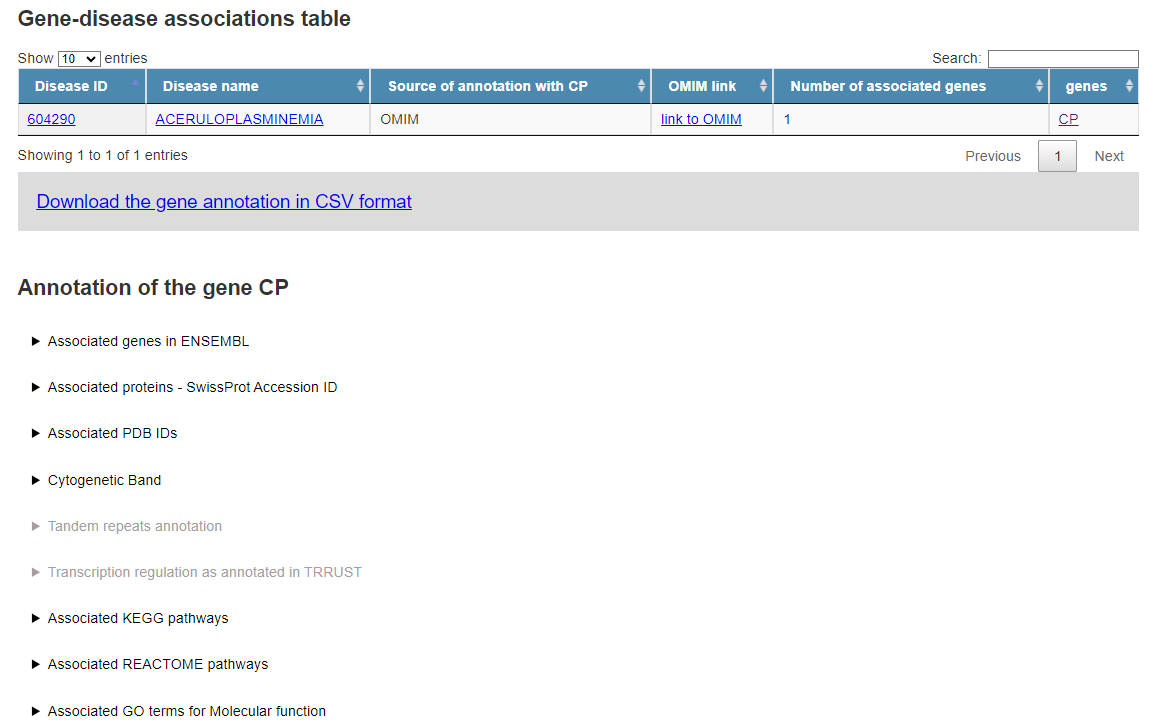
We retrieve all the possible diseases, in this case only "Aceruloplasminemia", with OMIM ID "604290".
It is a recessive disorder of iron metabolism characterized by iron accumulation in the brain as well as visceral organs.
Clinical features consist of the triad of retinal degeneration, diabetes mellitus and neurological disturbances.
Among the others, the result page (Figure 3) contains the link to the UniProt webpage, containing al protein variants, and the PDB identifier for the available structure.
KEGG and Reactome pathways, GO terms, Trascription Factors and gene annotation as cytogentetic bandem or tandem repeats are reported, if available.
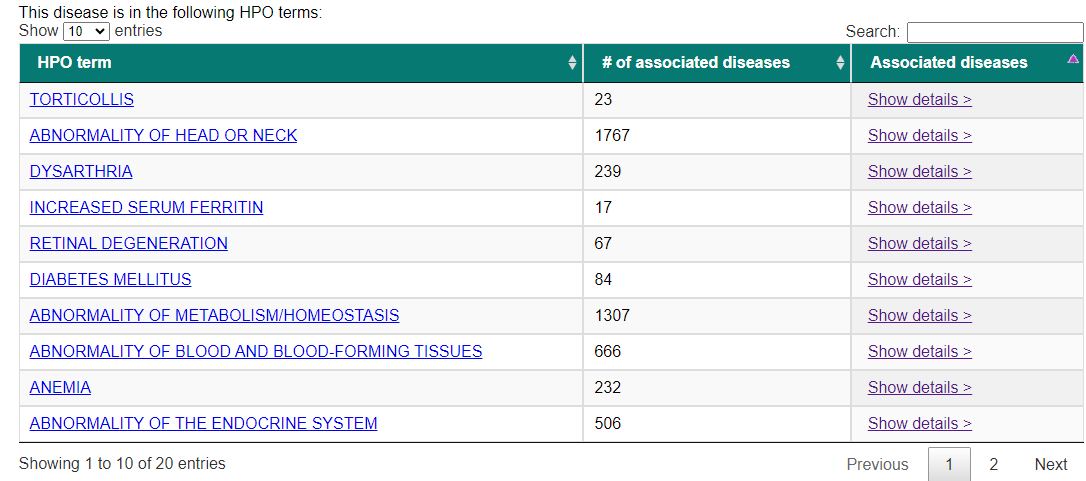
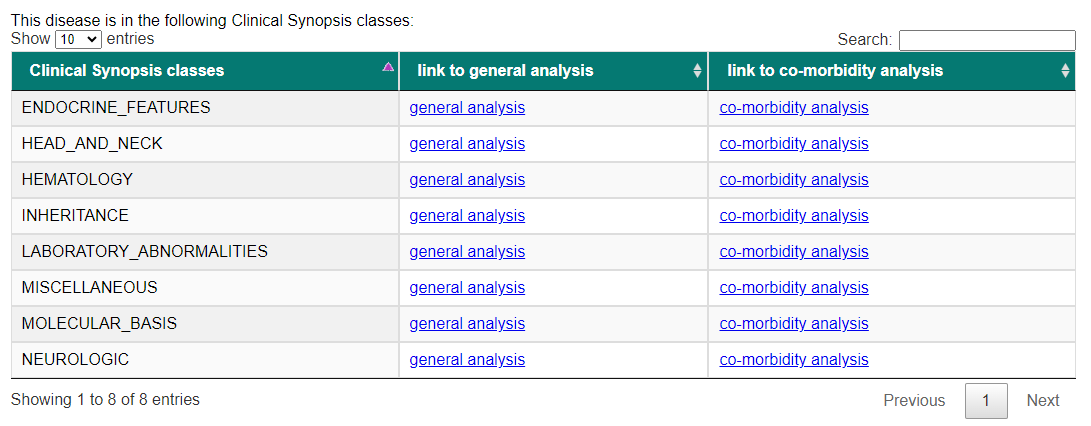
We may use PhenPath to retrieve more details about this specific disease, using as input for our search the OMIM ID "604290".
In Figure 4 we see the results as a table listing all the related HPO terms along with the number of times we found each term associated with a disease,
while Figure 5 shows the Clinical Synopsis classes related to the disease in input.
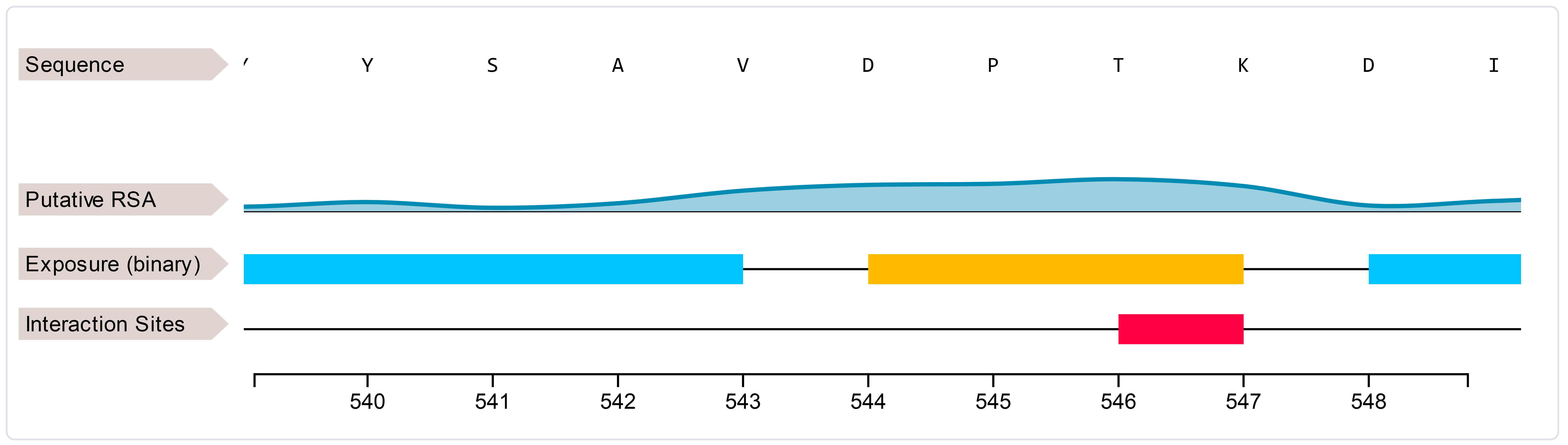
We focus our analysis on a specific position of the protein, the residue of aspartic acid in position 544,
that is known to be related with a reduced ferroxidase activity when mutated in glutamic acid (D544E).
First, we start our analysis as if we have no clue of the protein structure, submitting this protein sequence to E-pRSA to see te predicted Relative Solvent Accessibility (RSA)
of position 544.
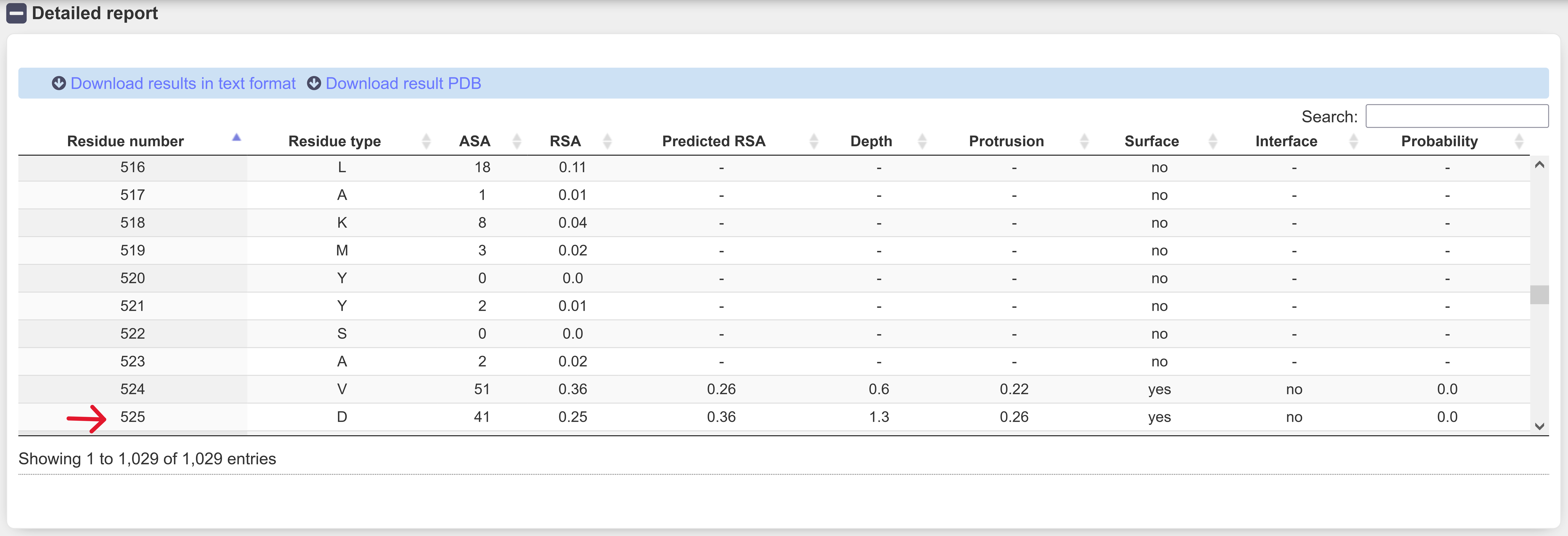
The position is predicted to be exposed and quite near an interaction sites (Figure 6).
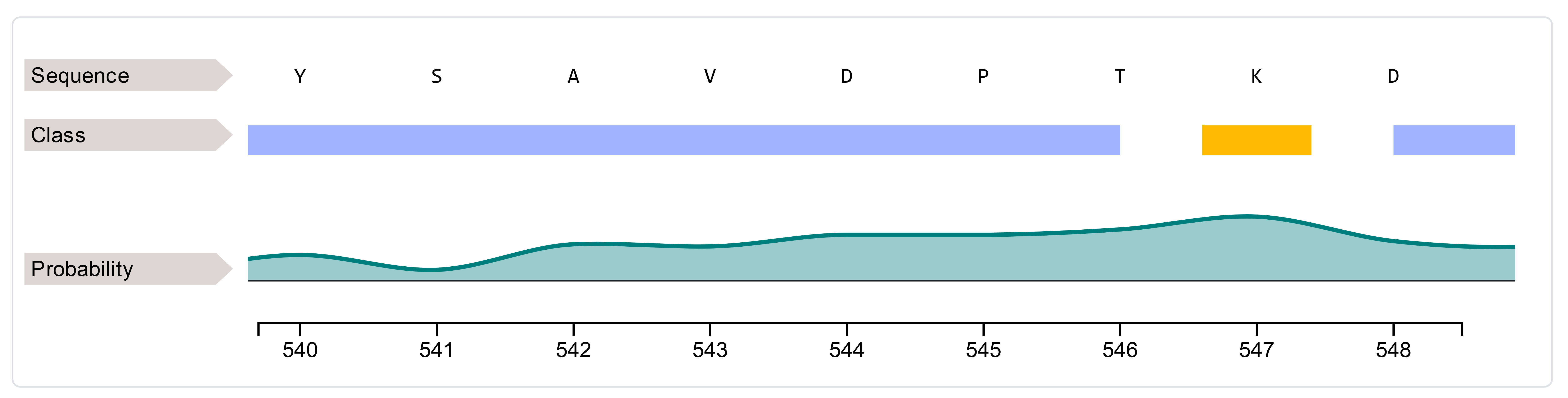
We may confirm this prediction with ISPRED-SEQ and ISPRED4, that predict the position as a surface residue not participating in direct interface (Figure 7 and 8)
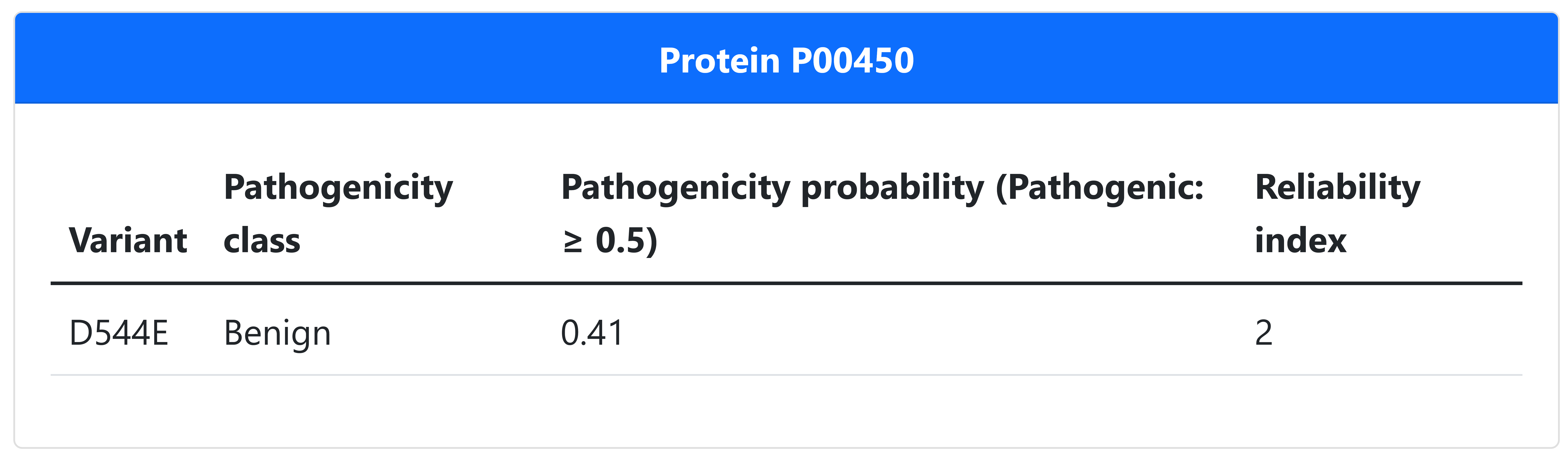
E-SNPs&GO is the used to predict the variant pathogenicity, conferming that the variant is Benign as reported in the literature, but with a very low Reliability index (Figure 9).
Still, the activity of the enzyme is partially reduced.
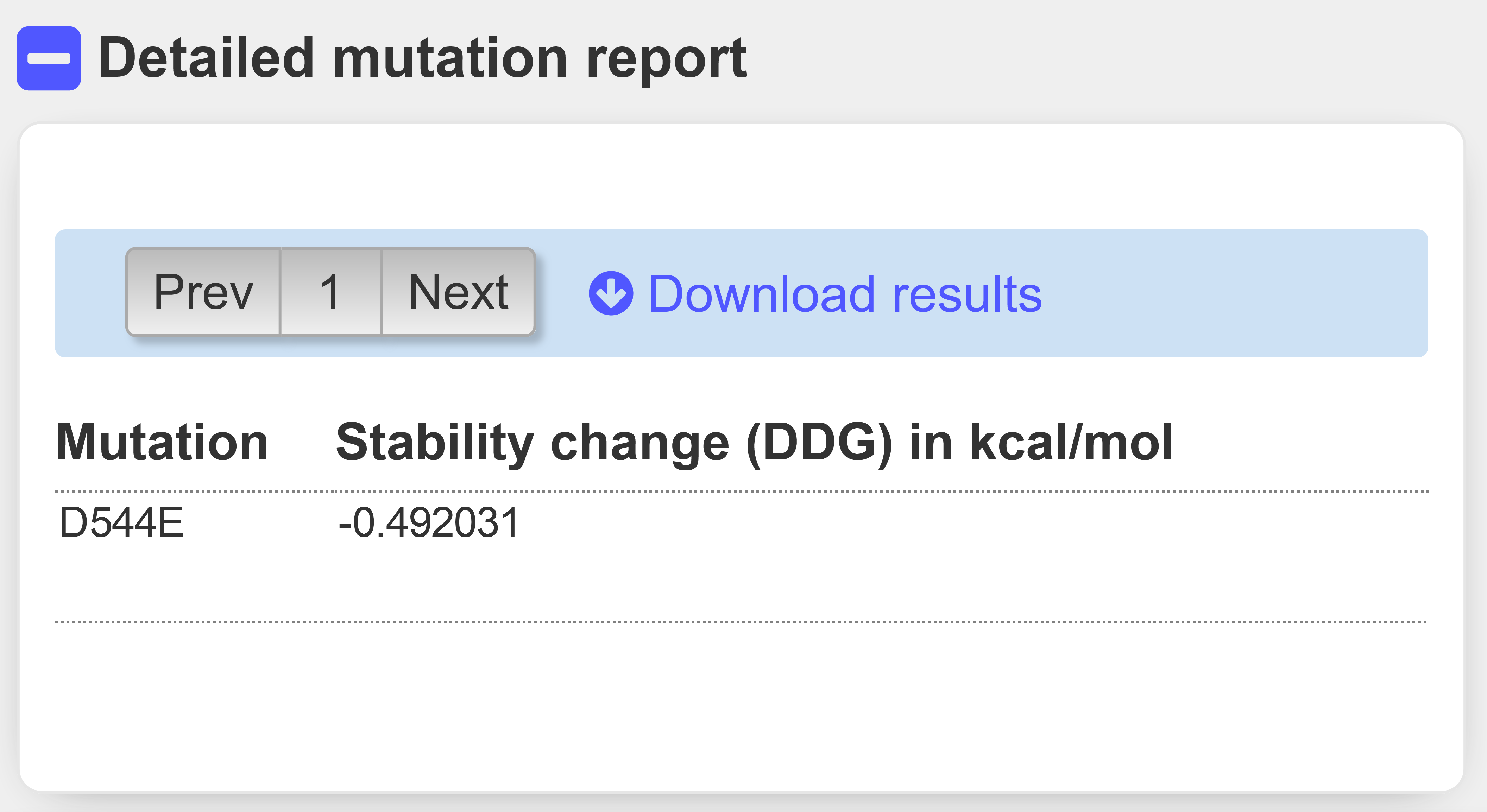
We may then investigate the impact of the variant on protein stability using the INSP-SEQ and INSP3D predictors, starting from sequence or stucture, respectively.
INPS precict a stability change of -0.49 kcal/mol (Figure 10). It is not a stabilizing variants, neither it is destabiling the whole protein folding.
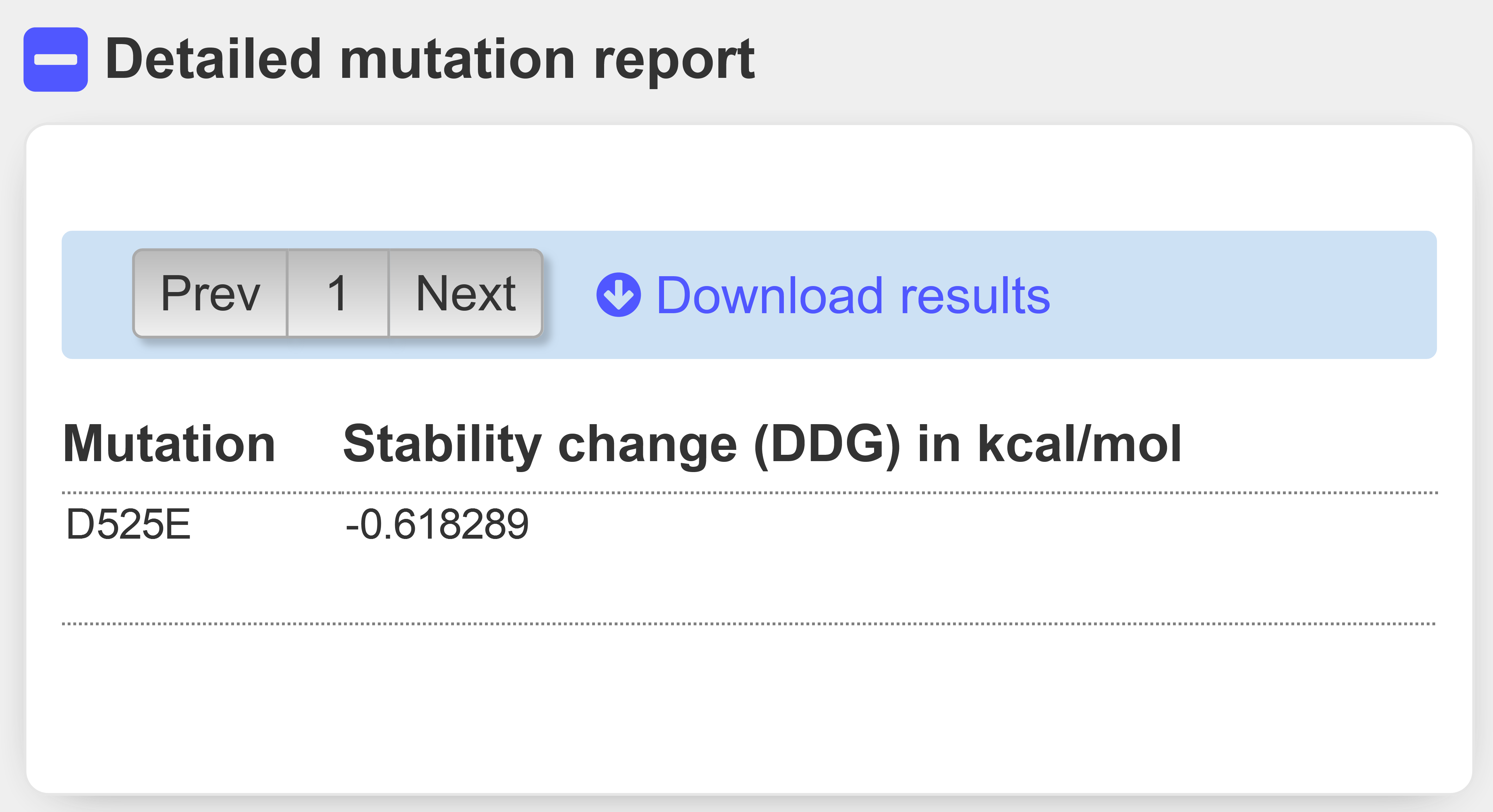
INSP-3D precict a slightly higher stability change of -0.62 kcal/mol (Figure 11), confirming precedent results.
Finally, we may search in MultifacetedProtDB to retrieve information about other functionality of our protein.
It is involved in iron transport across the cell membrane. It provides Cu2+ ions for the ascorbate-mediated deaminase degradation of the heparan sulfate chains of GPC1.
It may also play a role in lung development or antioxidant defense, expecially in pulmons.
The list of all the possible annotation fields is reported in Figure 12.